1. Understanding Basic Concepts
What is an IP Address?
Think of an IP address like your home address or phone number. When you go online, every website can “see” your IP address, just like a delivery person knows where your home is.
According to Wikipedia’s definition:
An IP address (Internet Protocol Address) is a numerical identifier assigned to each device on a computer network. It is used to identify and locate devices on the network, allowing data to be routed correctly to its destination.
In simple terms, your IP address is your “ID card” on the internet. Websites use your IP address as one of several factors to evaluate whether a request is legitimate. Beyond IP address, websites also examine other indicators like browser fingerprint, behavioral patterns, and HTTP headers when deciding whether to allow access.
—Dedicated IP vs Shared IP – The Difference Matters More Than Type
| Feature | Shared IP | Dedicated IP |
| Definition | A standard VPN node shared by hundreds or thousands of users | An exclusive IP address used by you alone |
| Who Controls IP Trust | Determined by the behavior of other users, you cannot control it | Completely determined by your own behavior, you have full control |
| Impact of Other Users | If someone misuses this IP, all users will be affected | No other users, so you won’t be affected |
| Stability | Poor—depends on the behavior of thousands of other users | Good—depends only on your own behavior |
| Analogy | Hundreds of people sharing one phone line; any improper behavior by one person affects the entire line | You have a phone line exclusively for yourself; other people’s behavior won’t affect you |
Core Conclusion: Before choosing between Datacenter and Residential IP, make sure you’re buying a dedicated IP, not a shared IP. This is more important than choosing the IP type.
—2. Understanding the Two IP Types
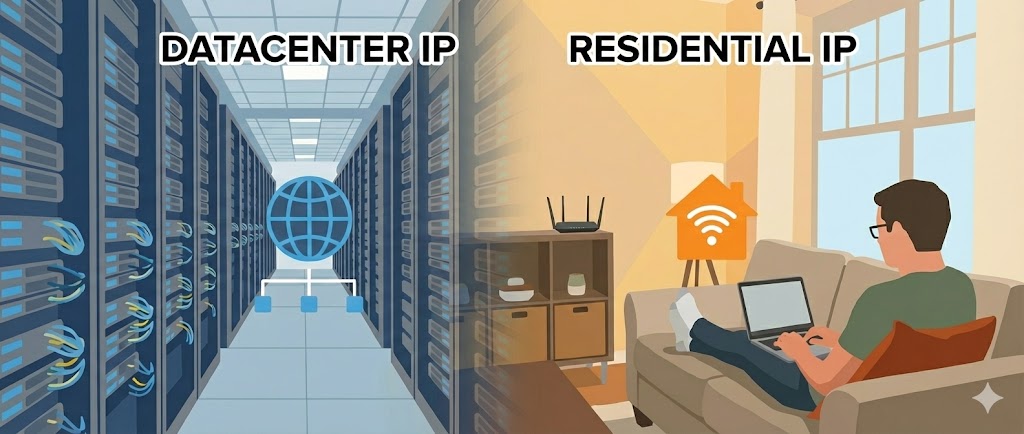
Datacenter IP
What is Datacenter IP?
Datacenter IP comes from servers of large companies, such as Amazon AWS, Google Cloud, Alibaba Cloud, Tencent Cloud, etc. The “identity information” of these IPs is public, and IP databases can identify that you’re using a cloud server.
How do websites identify it?
Websites query IP databases to determine whether an IP is hosted in a Datacenter. If they discover it’s a Datacenter IP, websites may reject the request, request additional verification, or flag it as suspicious traffic.
Advantages:
- Fast speed (short response time)
- Good stability (from professional Datacenters)
- Relatively low cost
Disadvantages:
- Websites can identify through IP database that this is a Datacenter IP, not a real user’s home network
- Many websites will reject Datacenter IP requests (such as Netflix, some banks)
- If it’s a shared version, it will be misused by other users, causing the entire IP to be rejected by websites
Applicable Scenarios:
- Accessing most public websites
- API calls and backend services
- Scenarios where you don’t need to be identified as a real user
- When budget is limited, choosing a dedicated Datacenter IP is more reliable than a shared Residential IP
Residential IP
What is Residential IP?
Residential IP comes from real home users. When you use the internet at home, your IP is a Residential IP. Sources include AT&T, Comcast, Verizon (USA) and other local telecom companies that allocate IPs to home users.
How do websites identify it?
Websites query IP databases and identify that the IP belongs to a local telecom company (such as AT&T, Comcast). Websites may be more lenient with it and perform less strict anti-bot or anti-fraud checks. However, this doesn’t guarantee access—websites may still reject it.
Advantages:
- Compared to Datacenter IP, it’s harder for websites to identify as a proxy or automated tool
- Access success rate may be higher on some websites
- May be helpful for scenarios requiring account login
- For websites with anti-bot protection (such as some e-commerce platforms), it may be easier to pass initial checks than Datacenter IP
Disadvantages:
- Cost is higher than Datacenter IP
- Speed is limited by real household broadband, which may not be as stable as Datacenters
- IP supply in some regions may be insufficient
- If it’s a shared IP, it will be affected by the behavior of other users
Applicable Scenarios:
- E-commerce operations: Managing multiple Amazon/eBay accounts, listing products, monitoring prices
- Social media operations: Operating multiple Instagram/Facebook/TikTok accounts
- Live streaming platforms: Providing live streams from different regions, managing multiple accounts
- Websites with active bot protection: Datacenter IP is detected and rejected
3. Why is Dedicated IP More Important Than IP Type?
Many users report “I bought a Residential IP but still got rejected by websites” or “My IP worked today but was blocked tomorrow.” Possible reasons include:
- Abnormal behavior during use causes website detection (such as requests that are too frequent, unusual access patterns, etc.)
- The IP purchased is shared, and other users’ misuse causes the IP to be blocked
- The IP purchased has poor quality or is already on blacklists
The Key Point: Dedicated IP
If you purchase a shared IP (standard VPN node), your access success rate will be affected by the behavior of thousands of other users simultaneously using that IP. Once any user misuses the IP, everyone will be affected. In comparison, dedicated IP has better stability because only you control the behavior of this IP.
Key Conclusion:
- Dedicated IP is more important than IP type (Datacenter vs Residential)
- A dedicated Datacenter IP is usually more reliable than a shared Residential IP
- Before choosing an IP type, make sure you’re buying a dedicated IP
4. How Do I Know What Type of IP I Have?
Wondering what type of IP you have? It’s easy—simply use one of the free IP detection websites below.
Recommended Free IP Detection Websites
- IP2Location
Enter your IP and it will display ISP, IP type, city, and country. - MaxMind GeoIP Lite
A professional IP database company providing free and paid IP identification services. - ipapi.is
Clean and intuitive, displays ISP and IP type. - whatismyipaddress.com
Simple and easy to use, suitable for beginners, displays basic IP information. - AbuseIPDB
Shows whether this IP has been reported for abuse, used to determine if an IP is marked as untrustworthy.
How to Read Results
If it shows:
- ISP: “Amazon AWS” or “Google Cloud”
- Type: “Datacenter” or “Hosting”
- → This is a Datacenter IP
If it shows:
- ISP: “Comcast” or “AT&T” or “Verizon”
- Type: “Residential” or “Home User”
- → This is a Residential IP
How to verify: Check using multiple websites simultaneously, as different websites’ databases update at different speeds. If 3 or more websites consistently show it as a Datacenter IP, you can confirm it’s a Datacenter IP.
—5. Why Are Detection Results Sometimes Inaccurate?
You may encounter a situation where Website A shows a Datacenter IP while Website B shows a Residential IP. Why the difference? There are several reasons:
1. Database Updates Are Slow
IP databases are not real-time. A newly allocated IP may take several weeks to be recorded in all websites’ databases. Therefore, new IPs are often mislabeled.
2. Accuracy Varies Between Databases
Large companies (such as MaxMind, Cloudflare) invest significant resources in maintaining IP databases. Small websites may use outdated data or third-party data, resulting in lower accuracy. This is why MaxMind’s data is usually most reliable.
3. IP Ownership Changes
An IP originally owned by AWS (Datacenter) may later be sold to a small ISP (potentially becoming Residential). Different databases update at different speeds, so you’ll see different results.
4. Geographic Location Information Lags
An IP’s geographic location information may be outdated. For example, an IP might show as being in the USA while the actual server is in Singapore.
5. Some Service Providers Claim to Offer False Labeling Services
Caution: Some unscrupulous IP service providers engage in false labeling claims:
- Claim they can falsely label Datacenter IP as Residential
- Or claim they can remove IPs marked as untrustworthy by websites from databases
The Reality: These IPs will eventually be identified and rejected by websites, because websites use multiple detection methods beyond IP database checks. Such services have limited effectiveness.
—6. Choosing IP: Considerations
IP Type Selection Framework
Scenario 1: You don’t need to be identified as a real user
If you only access public information and websites don’t care whether you’re a real user, you can consider Datacenter IP.
Scenario 2: You need to be identified as a real user, but have limited budget
If you need to be identified as a real user but have limited budget, you can first test with Datacenter IP. If rejected, upgrade to Residential IP.
Scenario 3: You need to be identified as a real user and have sufficient budget
If you need to be identified as a real user and have sufficient budget, you can directly choose a dedicated Residential IP.
Common Application Scenarios
- Scenario A: E-commerce Operations – Amazon/eBay Account Management
You need to operate multiple accounts, monitor prices, list products, and avoid account association.
→ Using a dedicated Residential IP may be more helpful - Scenario B: Social Media – Instagram/Facebook/TikTok Account Operations
You need to operate multiple accounts, publish content, and interact while avoiding account restrictions.
→ Use dedicated Residential IP - Scenario C: Live Streaming Platform – Twitch/YouTube Live Streaming
You need to provide live streams from different regions and manage multiple accounts.
→ Use dedicated Residential IP (for that region) - Scenario D: Data Collection – Competitor Price Monitoring
You need to collect competitor website data and avoid being detected or blocked.
→ Use dedicated Datacenter IP + proper HTTP headers + control request frequency - Scenario E: Public Information Access – Accessing Public Websites
You just want to access public information without login.
→ Dedicated Datacenter IP is sufficient - Scenario F: Website Has Bot Protection
The website you’re accessing has bot protection and Datacenter IP is rejected.
→ Test Datacenter IP first, then try Residential IP if rejected
One sentence summary: Make sure you choose a dedicated IP first, then select the IP type based on whether the website needs to identify you as a real user.
—Summary and Recommendations
Key Points Review
- IP is like your network identity: Websites can use IP to identify whether you’re a real user or a proxy.
- Datacenter IP’s identity is “public”: Websites can immediately see you’re using a cloud server proxy. Advantages: cheap, fast. Disadvantages: easily rejected.
- Residential IP is easier to be identified as a real user: It looks like a real user at home. Advantages: higher access success rate on some websites. Disadvantages: expensive, slow.
- Dedicated IP is more important than IP type: A shared Residential IP is not as good as a stable dedicated Datacenter IP. The key is to buy a dedicated IP, not a shared IP.
- There’s no perfect IP: Even a Residential IP will be rejected if websites discover it’s a proxy. Besides choosing the right IP, you also need to use it correctly (use correct HTTP headers, don’t access too frequently, add delays, periodically check IP quality).
Usage Recommendations
Consider:
- Choose IP type based on actual needs
- Prioritize buying dedicated IP rather than shared IP
- Use multiple websites to verify IP type
- Choose IP service providers that are transparent and have a good reputation in the industry
Facts You Should Know:
- False labeling services have limited actual effectiveness
- Detection results from a single website may not be accurate
- Residential IP cannot guarantee access to all websites
- Shared IP is affected by the behavior of other users
Core Point: IP type is one factor affecting access, but how you use the IP is equally important. Besides choosing the right IP type, you also need to use correct HTTP headers, control request frequency, and regularly check IP quality.
— John Wyatt
John Wyatt